Big Bang Theory is not what many think
What is this theory and its common misconceptions.
Answer and details at the end.
Imagine the universe as a tiny balloon. If you blow on the balloon, it will expand and get bigger. The Big Bang theory is like blowing on a tiny balloon, but instead of air, it was filled with all the matter and energy in the universe.
About 13.8 billion years ago, this tiny balloon started expanding (we don’t know why?), and it's been expanding ever since. As it expands, the universe cools, and it forms stars, galaxies, and planets. The Big Bang theory is the best explanation we have for how the universe began and how it has evolved over time.
Whatever the cause of the explosion, it's clear that something very special happened about 13.8 billion years ago. We are still learning about the Big Bang, and it's sure to be a mystery for many years to come.
Here are some of the key pieces of evidence that support the Big Bang theory:
Cosmic microwave background radiation (CMB)
The CMB is a faint afterglow of the Big Bang. It is a uniform radiation that fills the universe, and it is the oldest light in the universe. The CMB is one of the most important pieces of evidence for the Big Bang theory. It is consistent with the idea that the universe began in a very hot and dense state and has been expanding and cooling ever since.
The CMB was first discovered in 1964 by Arno Penzias and Robert Wilson, who were working at Bell Labs in New Jersey. They were using a radio telescope to study radio waves from the Milky Way galaxy when they noticed a faint background noise that was coming from all directions. This noise was later identified as the CMB.
The abundance of light elements in the universe
The Big Bang theory predicts that the universe should be mostly made up of hydrogen and helium, with smaller amounts of other light elements. This is exactly what we observe in the universe.
During the first few minutes of the universe's existence, the temperature was so high that protons and neutrons were constantly colliding and forming short-lived nuclei. These nuclei eventually combined to form stable isotopes of hydrogen, helium, and a small amount of lithium and beryllium.
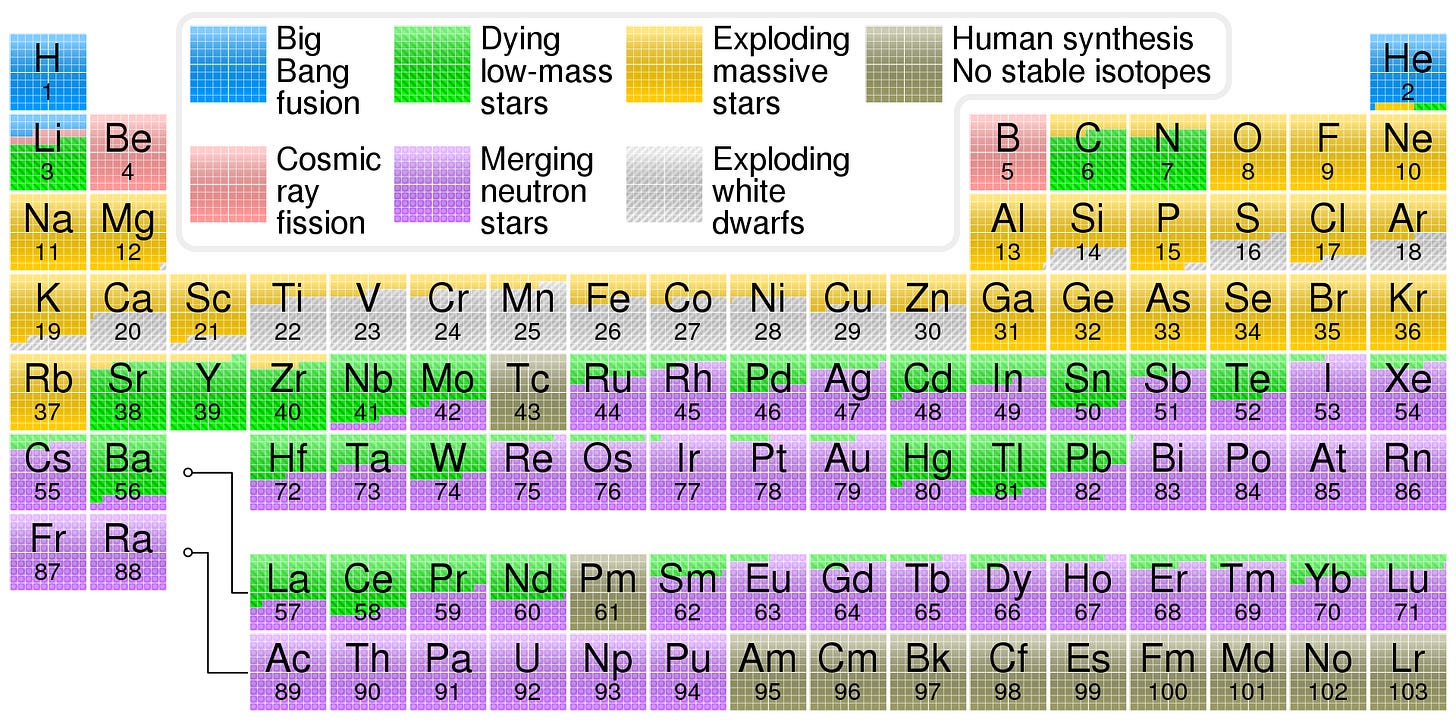
The observed abundance of light elements in the universe matches the predictions of the Big Bang theory with remarkable accuracy. Hydrogen accounts for about 73% of the mass of ordinary matter in the universe, helium accounts for about 24%, and lithium and beryllium make up only about 1% each.
If the universe had a different origin or if the nucleosynthesis process had proceeded differently, the abundance of light elements would be significantly different from what we observe. This consistency between theory and observation provides strong support for the Big Bang theory.
The redshift of distant galaxies
Redshift is a phenomenon in which light waves are stretched out, making them appear redder. To understand the connection between redshift and the Big Bang, consider the analogy of a car honking its horn as it passes you. As the car approaches, the sound waves are compressed, making the horn sound higher pitched. Conversely, as the car moves away, the sound waves are stretched out, making the horn sound lower-pitched, or redder.
Similarly, in the expanding universe, light waves emitted by distant galaxies are stretched out as they travel through the expanding space, causing their spectra to shift towards the red end. This observed redshift is directly proportional to the distance of the galaxy, providing a measure of how far away it is.
The redshift of distant galaxies has been observed for thousands of galaxies across the visible universe. This consistent pattern of redshift, with more distant galaxies exhibiting greater redshift, provides compelling evidence for the expanding universe and the Big Bang theory.
Misconceptions
There are several misconceptions and misunderstandings that often arise when discussing this complex theory. Here are some common misconceptions:
# 1: The Big Bang was an explosion from a specific point in space.
The Big Bang was not an explosion in space; rather, it was an expansion of space itself. The theory suggests that the universe began as an extremely hot, dense singularity and has been expanding and cooling ever since. It's not an explosion that occurred at a specific point but an expansion from an extremely compact state.
Remember our balloon analogy before? An exploding balloon and an expanding balloon are very different things, right?
# 2: The Big Bang theory explains the initial cause of the universe.
The Big Bang Theory explains the early development and expansion of the universe from an extremely hot and dense state. However, it doesn't address what caused the initial singularity or what happened before the Big Bang. It describes the evolution of the universe from an extremely early stage but doesn't delve into the origins or cause.
# 3: The Big Bang occurred as an event in a particular location.
The Big Bang didn't happen at a specific point within space; instead, it involved the entire universe. It's not an explosion in a specific area of space but rather an expansion of space itself, with galaxies moving away from each other in all directions.
# 4: The Big Bang produced an empty, space-filled universe.
Initially, the universe after the Big Bang was incredibly hot and dense, consisting of a hot soup of particles. It wasn't empty space but a state where matter, energy, and fundamental forces were unified. As the universe expanded and cooled, particles formed, eventually leading to the creation of atoms, stars, galaxies, and the structure we see today.
# 5: The Big Bang Theory proves the existence of a 'before.'
The concept of 'before' the Big Bang might not apply in the traditional sense, as time itself might have begun with the Big Bang. The theory's application to time might suggest that the notion of 'before' the Big Bang may not hold, given the absence of a temporal framework before the universe's inception.
Saying before Big Bang is similar to saying North of North Pole. Seems wierd right?
# 6: The Big Bang is just a belief system and not a theory supported by evidence.
The Big Bang theory is one of the most well-supported theories in science. It is supported by a wide range of evidence, including the cosmic microwave background radiation, the abundance of light elements in the universe, and the redshift of distant galaxies. It is not a belief system. It is a scientific theory that is based on evidence and observation. Scientists are constantly testing and refining the Big Bang theory, and it is one of the most successful theories in the history of science.
The Big Bang Theory has undergone refinement and adaptation over time based on observations and new scientific discoveries. While it's a highly successful and widely accepted cosmological model, there are still areas of speculation and ongoing research to better understand the early universe and its origins.
The total mass of all the asteroids combined is less than that of Earth's Moon. True or False?
True. The total mass of all the asteroids combined is only about 3% that of Earth's Moon. This is because most asteroids are very small, and they are spread out over a large area of the solar system.
The largest asteroid, Ceres, has a diameter of about 950 kilometers. Vesta is the second-largest asteroid, with a diameter of about 530 kilometers. For the context, the diameter of our Moon is 3,474.8 km





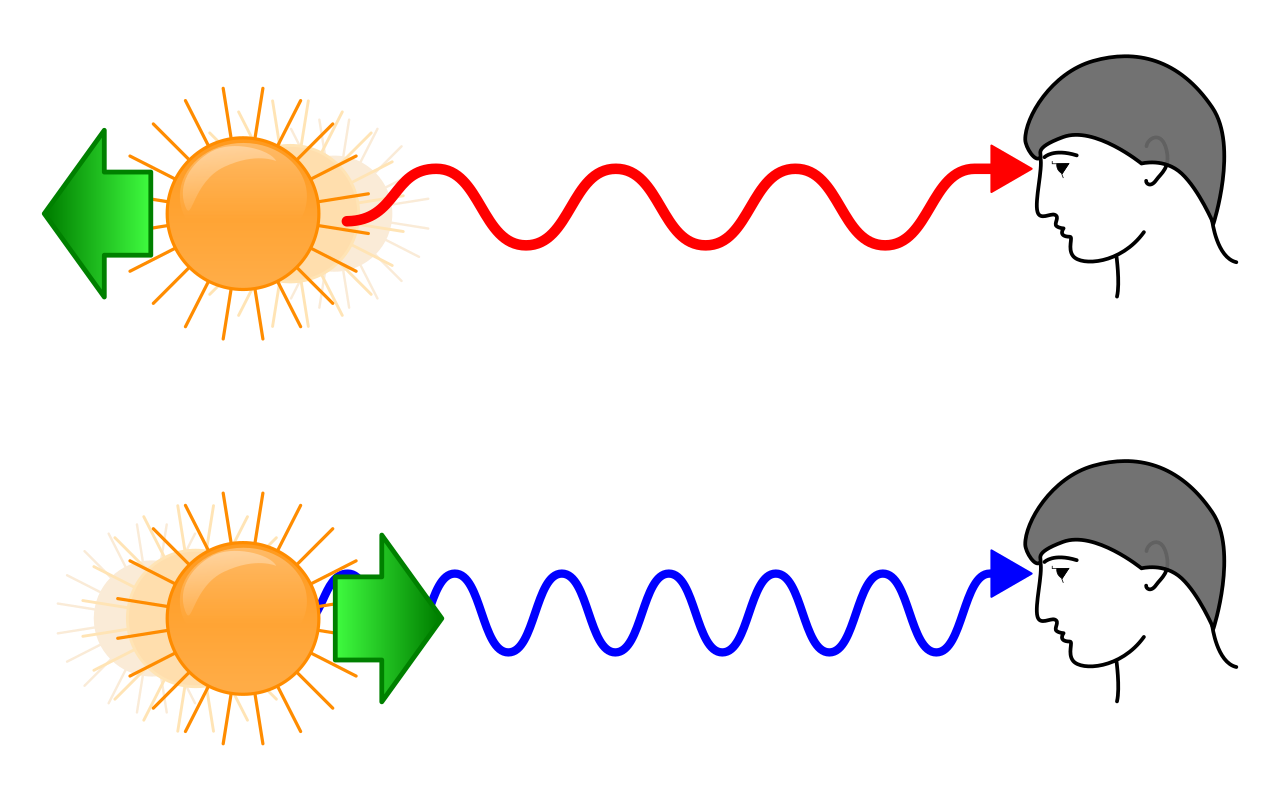

Very Informative and clear.